Waste Technologies
We make waste management more efficient
Technology enhances the circular economy model
We work on smart waste management to implement a more efficient operational model based on digital data collection and analysis
Our goal is to maximise the digitisation of the packaging life cycle
We consolidate the data generated throughout the various waste management stages (collection, treatment, and quality) into a single platform. Using Big Data, we process, analyse, predict, and automate this information to optimise processes.

Projects
The technology used transforms waste management into a more efficient operational model
1. Platform and data analysis: Smartwaste
An innovative digital application for the smart management of packaging collection, treatment, and recycling. Any operator involved in the process (public administrations, companies, startups, universities, or technology centres) can access the app to view any data they need to improve the service provided to citizens and develop models that increase its efficiency.
The platform enables us to generate statistics and reports to inform improvement decisions. Real-time data collection by SmartWaste generates objective information sourced from:
If you are a tech company, please contact us through this form to get your seal.
2. Collection
In this operational phase, waste is transported from containers to sorting plants. Our projects in this area focus on analysing the data collected by SmartWaste:
3. Treatment
The processes that take place once the waste reaches the sorting plants, where it is separated based its material composition, are continuously optimised:
Digitalization of operations in sorting plants
Implementation and validation of real-time data collection systems allow for optimal equipment management and maintenance in the plants.

Digital twins
Virtual representation and digitisation of sorting plants enable us to analyse potential improvements without interrupting their operation.
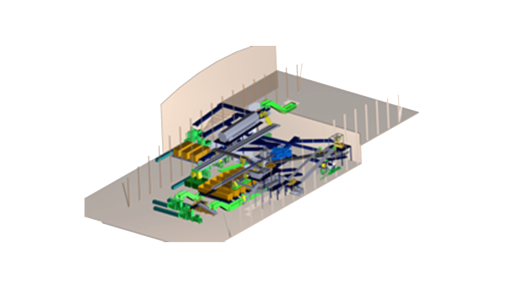
Varpel
Artificial vision techniques achieve maximum efficiency in the sorting process through the calculation of waste density and volume.
4. Quality and traceability
We drive the development of technological projects to improve service quality:
Place yourself on the circular economy map
Close the circle. Join the digitisation of circular cities
Help us create a more circular society
Would you like to be part of one of our projects?
